Motional EMF
Motional EMF: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Motion of Conducting Rod in Earth's Magnetic Field and Various Cases,Energy Conservation in Electromagnetic Induction as Quantitative Analysis,Motional Emf in a Rotating Conducting Disc etc.
Important Questions on Motional EMF
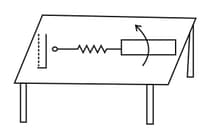
The figure given below shows an arrangement by which current flows through the bulb (X) connected with coil B, when a.c. is passed through coil A.
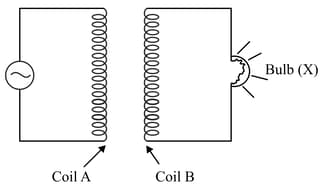
(i) Name the phenomenon involved.
(ii) If a copper sheet is inserted in the gap between the coils, explain how the brightness of the bulb would change.
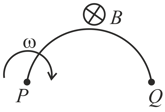
A conducting rod of length rotates with a uniform angular velocity about its perpendicular bisector. A uniform magnetic field exists parallel to the axis of rotation. The potential difference between the two ends of the rod
A metallic rod of length is rotated with a frequency of revolution per second, with one end hinged at the centre and the other end at the circumference of a circular metallic ring of radius about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the ring. A constant uniform magnetic field of parallel to the axis is present everywhere. The emf between the centre and the metallic ring is
The spokes of a wheel are made of metal and their lengths are of one metre. On rotating the wheel about its own axis in a uniform magnetic field of tesla normal to the plane of wheel, a potential difference of is generated between the rim and the axis. The rotational velocity of the wheel is
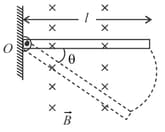
A conducting rod of length is hinged at point . It is free to rotate in vertical plane. There exists a uniform magnetic field in horizontal direction. The rod is released from position shown in the figure. When rod makes an angle from released position then potential difference between two ends of the rod is proportional to:
The figure shows a rod of length with points and on it. The rod is moved in a uniform magnetic field in different ways as shown. In which case, the potential difference between and is minimum?
A thin semicircular conducting ring () of radius is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field , as shown in the figure. The potential difference developed across the ring whẹn its speed is , is:
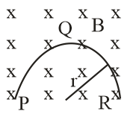
A metallic rod of length is tied to a string of length and made to rotate with angular speed on a horizontal table with one end of the string fixed. If there is a vertical magnetic field in the region, the e.m.f. induced across the ends of the rod is:
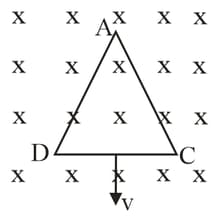
An equilateral triangular loop having some resistance is pulled with a constant velocity out of a uniform magnetic field directed into the paper. At time , side of the loop is at the edge of the magnetic field. The induced current versus time graph will be as
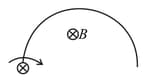
A conducting ring is placed in a uniform magnetic field with its plane perpendicular to the field. An emf is induced in the ring if
A semicircular wire of radius is rotated with constant angular velocity about an axis passing through one end and perpendicular to the plane of the wire. There is a uniform magnetic field of strength . The induced e.m.f. between the ends is:
A rectangular coil has turns and its length and width is and respectively. The coil rotates at a speed of rotation per minute in a uniform magnetic field of . Then the maximum induced emf will be-
When a magnet moves near a conducting coil, a current gets induced in the coil. What is the source of this electrical energy generated in the coil?
A copper rod of length is rotated about one end, perpendicular to the magnetic field , with constant angular velocity . The induced emf between the two ends of the rod is,
A wheel with metallic spokes each long is rotated with a speed of in a plane perpendicular to a magnetic field of The induced emf between the axle and rim of the wheel will be,
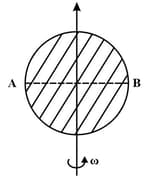
If a disc is rotated about its axis and if magnetic field is uniform and along the axis of rotation than what the potential difference between the edges of diameter -
A metal conductor of length rotates vertically about one of its ends at angular velocity radian per second. If the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is then the emf developed between the two ends of the conductor is
A metallic rod of length is rotating about perpendicular bisector of the rod with angular velocity of in presence of transverse magnetic field of . Potential difference developed across ends of rod is
A wire is bent to form a semicircle of radius . The wire rotates about its one end with angular velocity . Axis of rotation being perpendicular to the plane of the semicircle. In the space, a uniform magnetic field of induction exists along the axis of rotation, as shown in figure. Then